How to create a woodland fern garden (in big and small yards)
Even today's smaller backyards have room to create a native fern garden. Whether you have a small or large backyard, a fern garden will bring a sense of solitude to your woodland wildlife garden. These garden tips and ideas will help beginners and experienced gardeners plan, design and create the perfect fern garden in a corner of their yard to attract birds and other backyard wildlife.
How to use a variety of ferns to create a tranquil garden
It all started with a few ferns from a friend at work and a warning about how fast they can take over.
Today those ferns have grown into a massive backyard fern glen and I have tapped into the huge variety of ferns that are available to gardeners. The number of fern varieties is endless, from tiny ones that go unnoticed in the landscape to huge tree ferns that grow in more temperate climates.
(More on the variety of ferns available lower down in this post.)
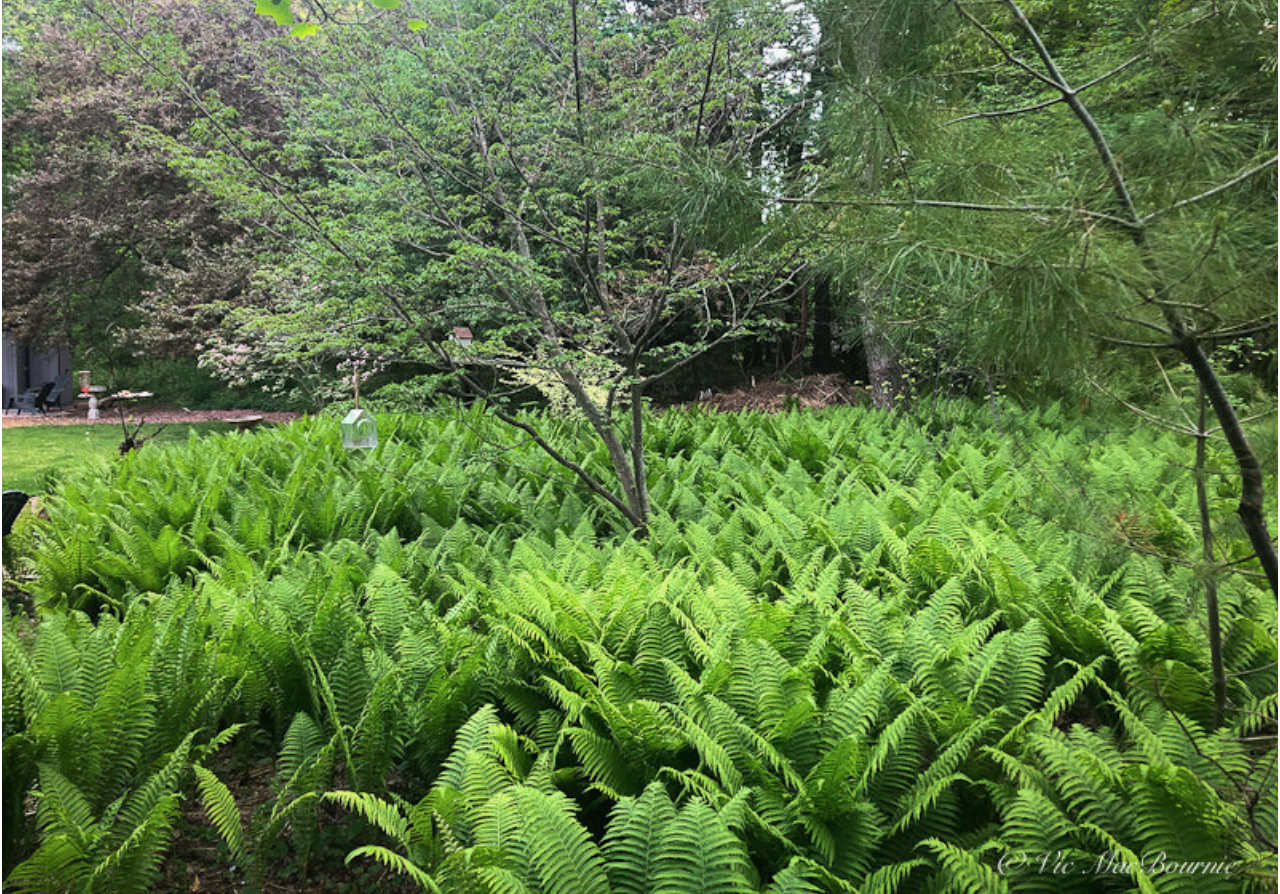
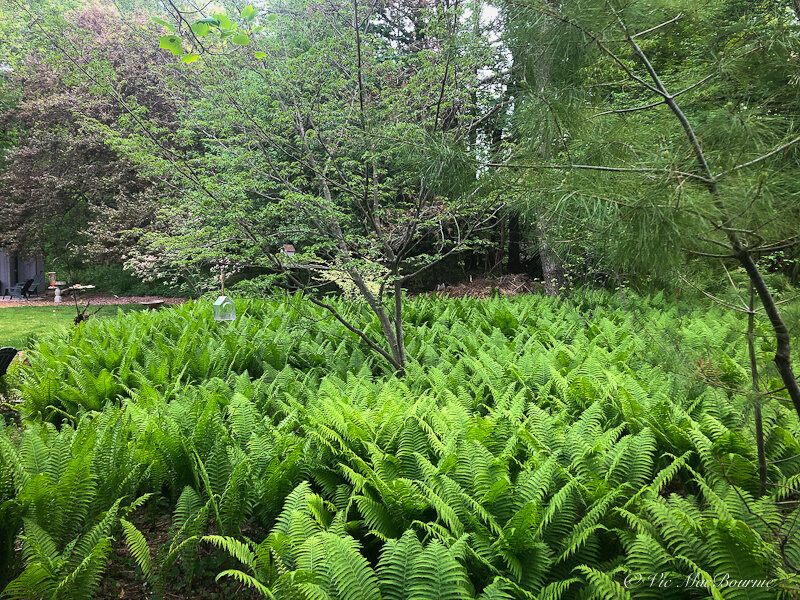
Back to the ostrich ferns given to me by a co-worker. Knowing that I had a large expanse of grass on one side of our pie-shaped lot that could use a nice little garden of wildflowers, ferns and shrubs, I went to work.
That was maybe 15 years ago.
Little did I know then that this little garden would, in relatively short order, become the focal point of our woodland wildlife garden, providing endless joy in spring and summer not only for me, but for the myriad of wildlife that can easily get lost in its hundreds, heck maybe thousands, of massive ostrich ferns.
If you are interested in exploring the world of shade gardening further, you might like my recent post on The Natural Shade garden.
If you want even more information on ferns, you might want to explore the book The Plant Lovers Guide to Ferns.
Why create a Fern Garden?
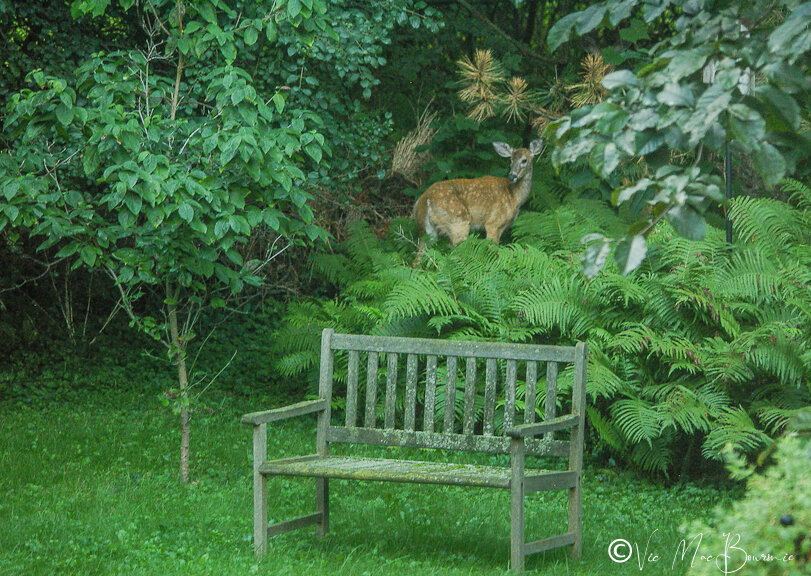
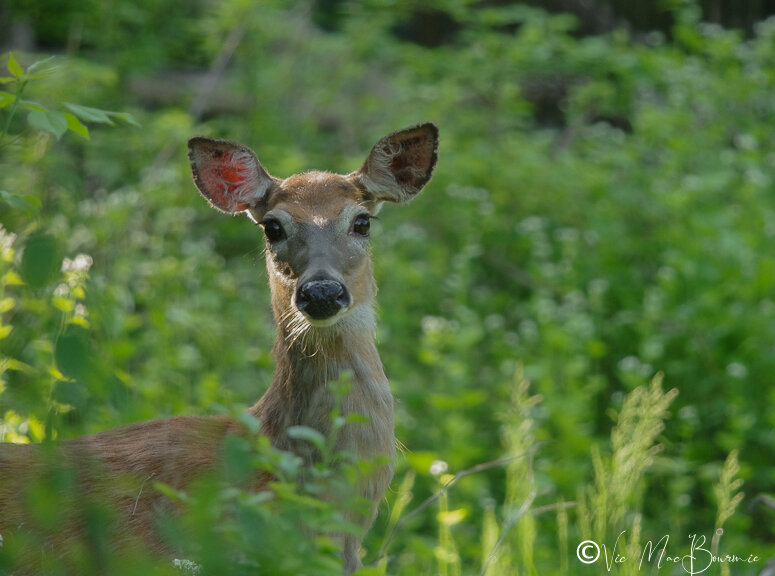
The fern garden has become a favourite place for deer to hide their youngsters during hot summer days. I know the resident fox has used it as a secret roadway into the main garden emerging, as she often does, from the middle of the fern glen. I have come across shedded snake skins among the spent ferns in the fall and watched countless chipmunks scamper into the cool surroundings of the ferns on hot days. It’s a home for toads and salamanders seeking deep shade during the heat of the day and creates the perfect backdrop for the under story trees and shrubs that grow up through the ferns in our woodland wildlife garden.
One day I even decided to get down low and crawl through the maze of ferns to get the same view as the animals that call it home.
To say it’s a whole new world in there is a huge understatement, and I can only imagine the young fawns thinking they are giants in a miniature, prehistoric forest.
If you are looking to add plants to your garden this year, consider planting seeds to help you fill out bare spots in your garden beds. Use this link to get 20 per cent off your next seed order from Burpee Seeds.
How do ferns help wildlife?
Anne Owen, an Audubon at Home Ambassador with the Loudoun Wildlife Conservancy, in her article Native Ferns Have a Place in Our Plantings for Wildlife writes that “From a wildlife point of view, ferns can give structure that provides foraging space and shelter for ground-feeding birds, while other critters, for example frogs and turtles, like to hide in them. Ferns are generally resistant to browsing by rabbits.” (For the complete post go here.)
Oh, and let’s not forget the best reason for many of us to grow a fern garden: Deer leave ferns alone. Anything deer prefer to leave OFF their dinner diets is definitely worth growing in a woodland garden.
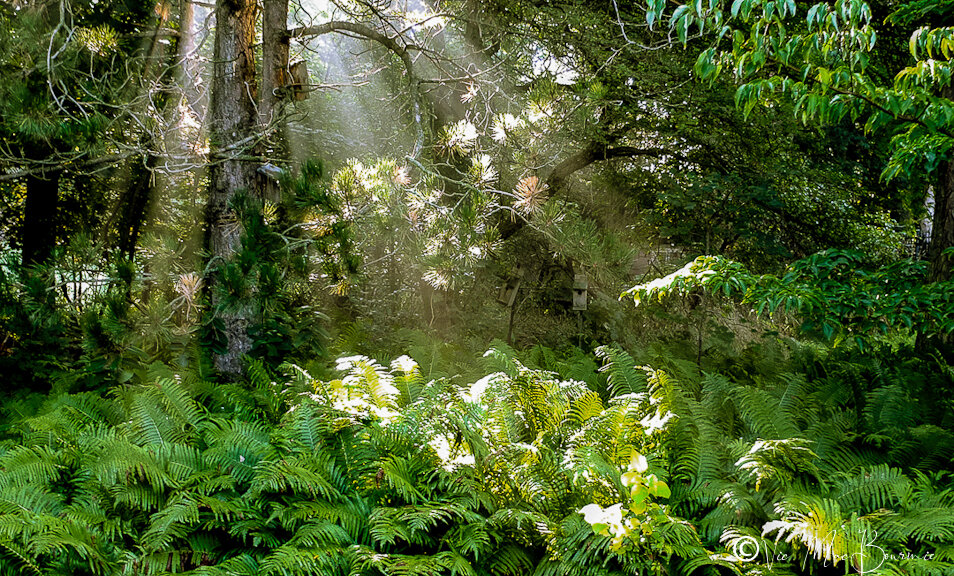
We are blessed with a good-sized property and are able to set aside a large portion of it for the establishment of a fern glen. I realize many gardeners either don’t have the space, or don’t want to donate that amount of space to create such a huge expanse of ferns in their backyard.
That’s no problem. A more compact fern garden in the understory can be just as rewarding.
How to create a fern garden in smaller yard
Obviously, in a smaller backyard the fern garden could be downsized to better fit into the proportions of the garden.
The quiet serenity that a fern garden can create is certainly incentive enough to begin planning for an area in the garden you can retreat to on hot summer days.
Building the right soil for ferns
If you can start with a rich, moist, earthy soil with plenty of decayed or decaying material in it, you are off to a good start. You can, however, build this soil over time by using the fern garden as a destination for all those leaves you collect in the fall and spring. Over time, the soil will build up an earthy layer of forest duff, perfect for growing woodland ferns.
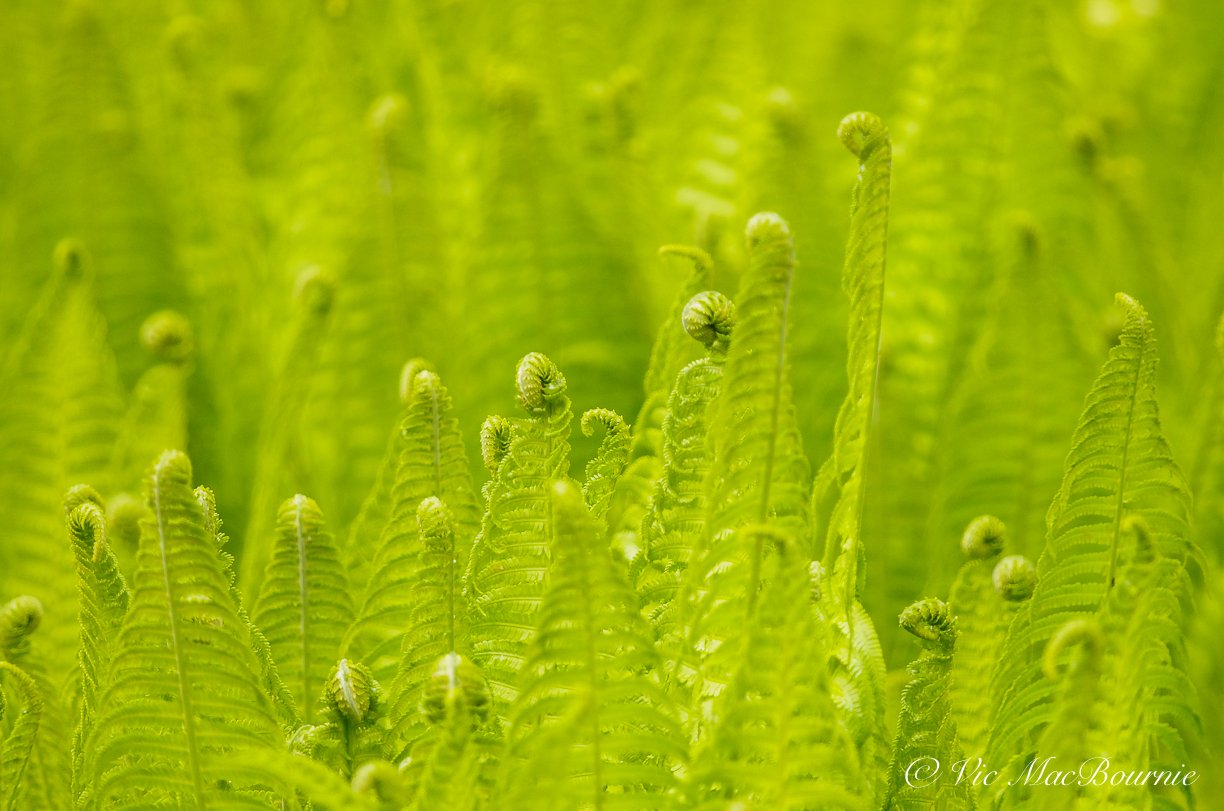
Our fern garden is the primary dumping ground for most of the fall leaves I pick up from the front yard. Each year it gets 5-10 bags of leaves dumped in various spots throughout the fern garden. In some areas the leaves are several inches thick, but that doesn’t stop the ostrich fern fiddleheads from popping up through them every spring.
I originally used the newspaper layering technique to give our fern garden a good start. My neighbour had at least ten bags of leaves that he had not put out by the curb in the fall. By the time spring rolled around they were a soggy mess of paper bags and partially decomposed leaves.
Perfect to give the fern garden a good start.
He happily accepted my request to take them off his hands and the project began.
A thick layering of newspapers to block the light and ensure a quick end to the grass, followed by a bags of fresh soil, ten bags of partially composted leaves and a handful (I think somewhere in the neighbourhood of 10-15 ferns) all nicely covered by several bags of cedar mulch, and the project was complete.
Or so I thought. Since then, the ferns have spread out from all directions multiplying each year to form the massive fern garden incorporating hundreds if not thousands of ferns.
How to use ferns as a ground cover
In the beginning days, the compact fern garden, (maybe 6-feet by 12 feet) centred around a young Cornus Kousa dogwood that I had planted that same year.
Today, 20 years later, that same Kousa dogwood is a spectacular mature specimen that stretches two-, maybe three-storeys high and probably 16-feet wide. Most years it puts on a show of creamy-white blooms that is simply breathtaking and the huge, red, strawberry-like fruit that follows are a favourite of local wildlife. (Check out my earlier post on six great dogwoods for the Woodland garden here.)
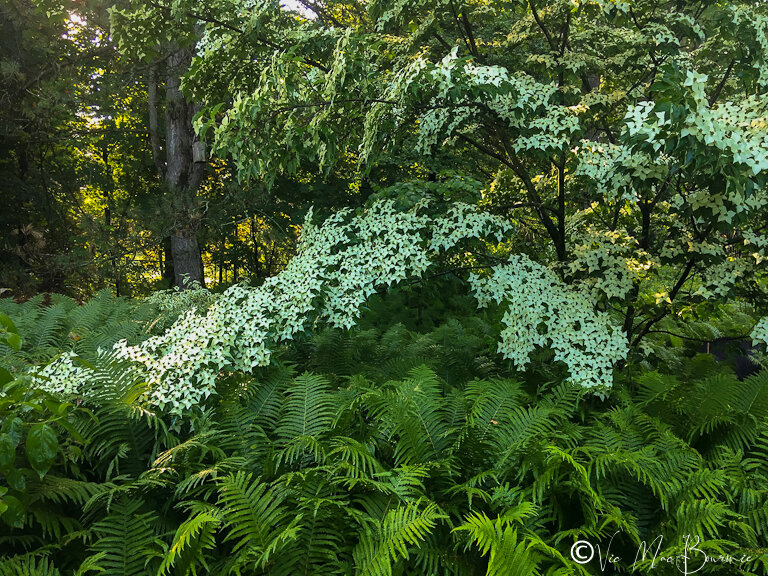






A quick note: In a smaller garden the Kousa dogwood can be kept pruned to some degree to keep it more compact. I am a big believer that, for the most part, trees should be allowed to grow into their natural shape. As a result, the Kousa dogwood, not unlike most dogwoods, takes on a very horizontal branching shape that I think gives it a Japanese-style look.
By simply taking a scaled-down approach in your smaller garden you can create a similar effect.
A few dozen of the more compact-style ferns scattered around a couple of your favourite understory trees such as a native flowering dogwood, or pagoda dogwood (see earlier post on three great Carolinian zone under story trees), or a native redbud tree (See earlier Redbud tree post here) can evoke that same peaceful feeling on a smaller scale and provide you with spring blooms and berries.
How ferns spread in the garden
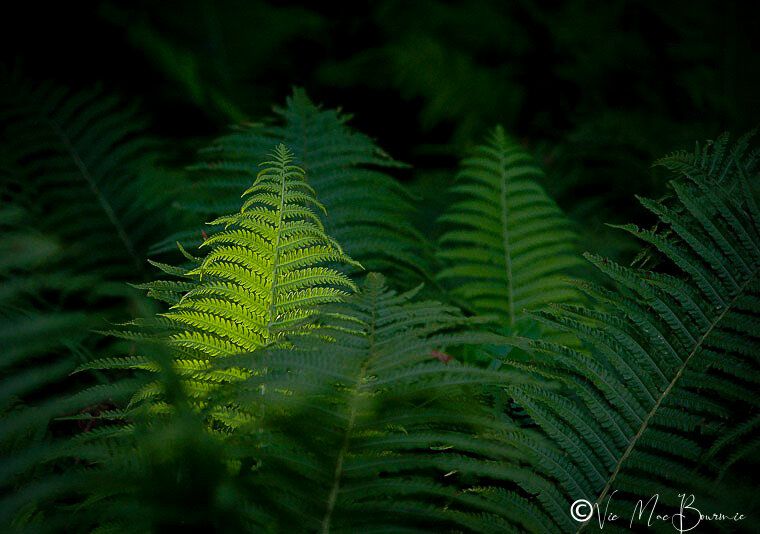
It’s important to note that ferns have two basic forms of growth: creeping (which includes our ostrich ferns) and crown-forming.
The creeping forms can spread through the garden at times aggressively from trailing rhizomes or stolons.
The crown forming ferns (such as maidenhair ferns) grow much in the same way as traditional perenials grow by expanding from the centre.
These ferns grow from upright rhizomes and carry their fronds in a tight circle.
These are important points when considering your choice of ferns and how much you want the garden to grow or the work you are willing to tackle to keep it contained.
Fern varieties to consider in a smaller garden
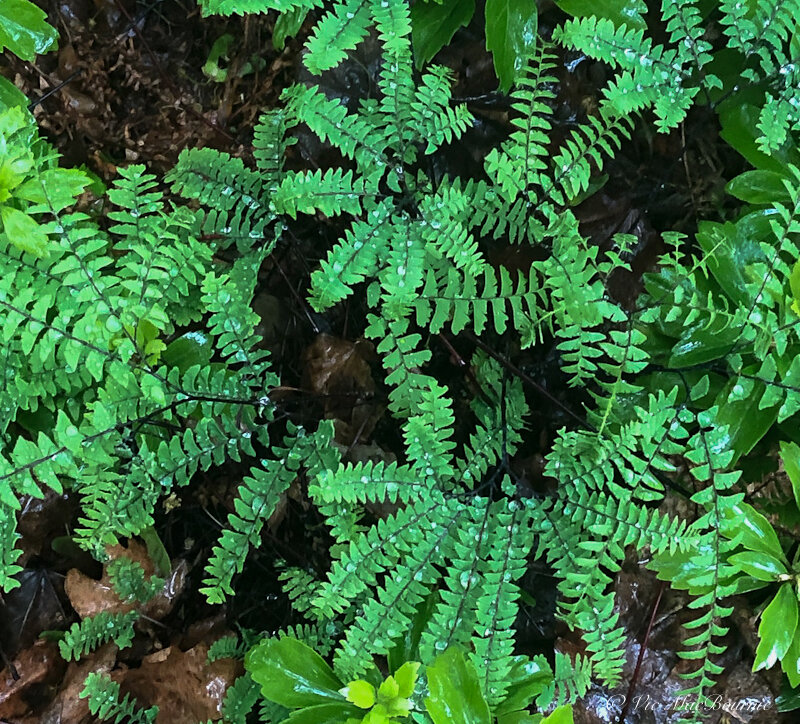
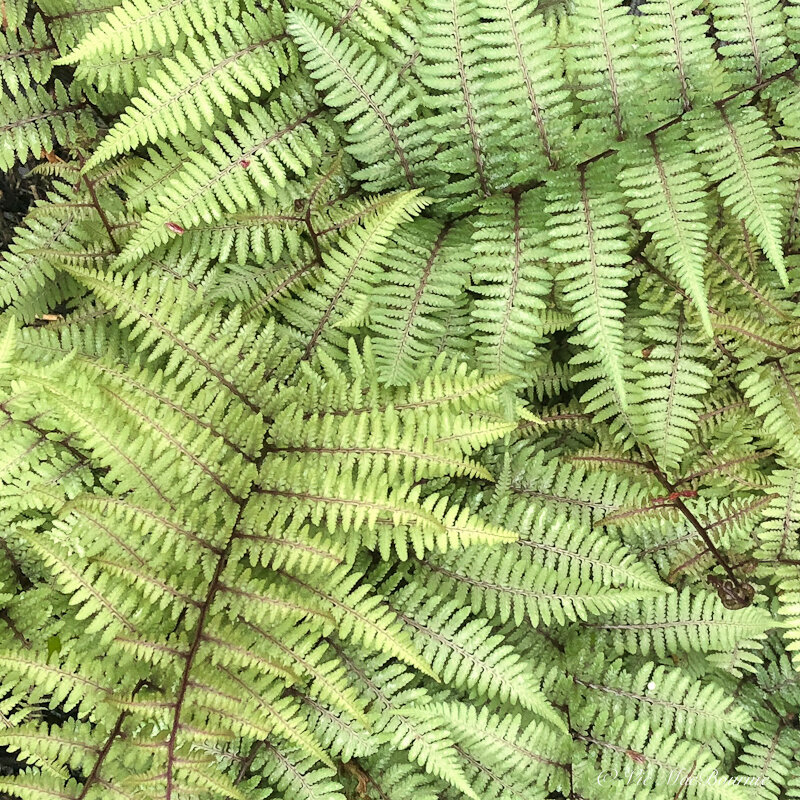
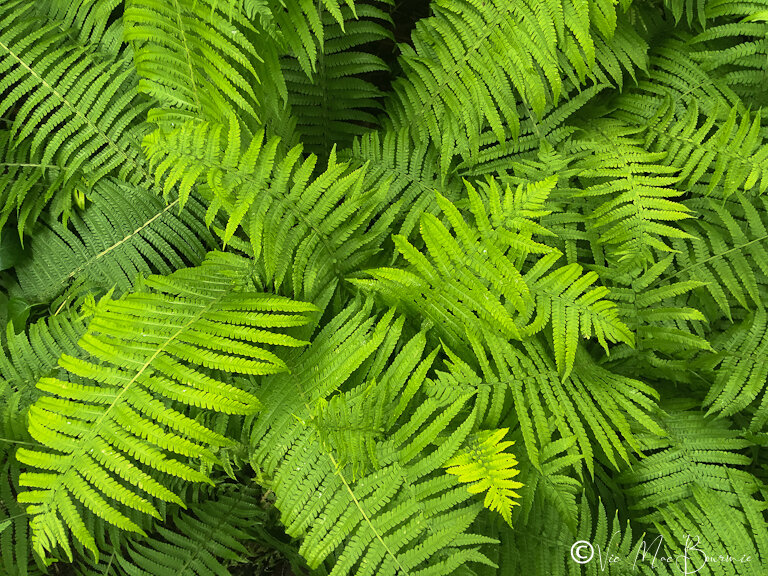
Ferns are available in such a variety of shapes and sizes, colours and textures that the selection is almost endless.
Consider using a combination of native and non-native ferns to create your fern glen. The following is a list of several native ferns that deserve top consideration in your garden. We use many of these ferns in our front woodland garden where there is less competition from the larger Ostrich ferns that dominate the back fern garden.
Maidenhair ferns: A hardy, yet delicate and graceful fern that is at home in any woodland setting with its charming whorl of light, gray-green feathery foliage that spreads in clump form and is at home in a range of soil conditions including growing near or even on rocks and areas with acidic soil. There are a number of maidenhair species (Northern, Southern, Rosy, Western and Silver dollar) to consider depending on the zone where you garden.
Wood Fern: (Dryopteris marginalis) This non-spreading fern sports graceful, arching gray-green fronds that form a vase-shaped clump. Expect about 24 inches in height and similar spread in this long-lived plant with dense foliage extending right to the ground. Enjoys part shade to full shade in a medium to wet organic loam and grows to about 2 feet.
Sensitive Fern: (Onoclea sensibilis) this interesting looking fern with its tender leaflets that close to your touch (hence the name) is readily propagated by spores and grows in large colonies in the wild. This light green fern is considered short-lived (10 years) but is quick to naturalize in woodland gardens and boggy areas with a definite preference for acidic soils.
Autumn fern: (Dryopteris erythrosora) a semi-evergreen fern (zone 5-9) with year-round interest. It’s attractive glossy ferny compound leaves emerge coral-pink in spring turning green with prominent coppery-bronze tips for the remainder of the year.
Growing to about 18 inches tall at maturity with a similar size spread, the Autumn fern is one of the few ferns that performs well in both full sun and full shade.
It prefers average to wet conditions and can even be grown in very wet areas tolerating some standing water. Grow it in rich, acidic soils in mass plantings, rock/alpine gardens or naturalized in a woodland garden.
Non-native ferns worth considering
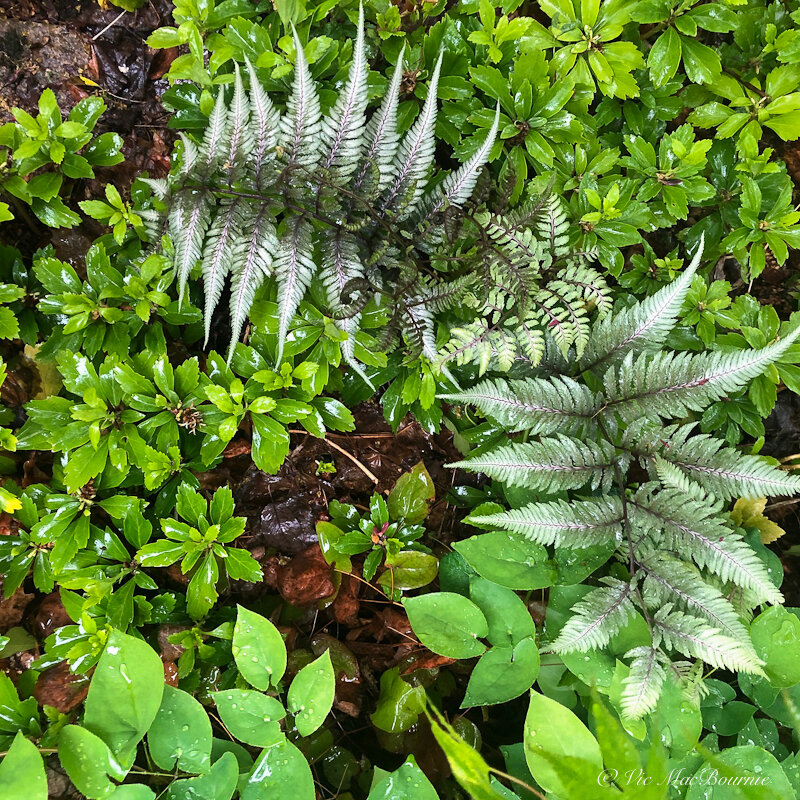
While it’s always best to use native plants, it’s hard not to include a few non-native ferns for the fern garden, especially the Japanese painted fern with it’s delicate silvery fronds that really is a showstopper in a shady area.
Japanese painted fern: Athyrium nipponicum ‘Pictum’ and its many hybrids (zones 4-8) shines in the woodland with its silvery, purple and burgundy foliage. Japanese painted ferns are among the best silver-leaved plants for the garden with the added bonus of creating a dense, fine-texture with their interesting colour patterns that look almost hand-painted.
Use them in mass planting, as a dense ground cover or naturalized in the woodland garden.
The main stems are an eye-catching burgundy colour that spills out into the silvery-gray fronds.
Like most ferns, they prefer a shady location, but because of its silvery fronds, the Japanese painted ferns can handle more sun than many other ferns.
Expect growth of about 18 inches in height with a spread of 24 inches. It’s a slow grower but can live up to 15 years in our cold climates.
Ghost fern: Athrium ‘Ghost’ is another fern to consider, and one that is actually related to the Japanese painted fern. This larger fern, hardy in zones 3-8, can grow to about 2 feet tall and is a combination of the best qualities of a Japanese painted and a Lady fern.
The fronds of the ghost fern are stunning in a shaded location with fronds that give off an almost frosty-white appearance to their rigidly upright look. It does best in partial shade with a moist, neutral to moderately acidic PH soil.
A little sun helps to bring out its best colouring and it can survive in drier soil than many other ferns.
Lady Fern: (Atthyrium felix-femina) is a favourite for those with sandy loam or clay loam where this tough fern will grow quite willingly to about 3 feet in height.
Ground covers to highlight your fern collection
Ferns can work both as a ground cover or as the focal point in the fern garden.
In my fern garden they work more as a very tall ground cover and form the backdrop for the dogwood, serviceberries, redbud, white pine, spruce trees trees and shrubs that grow up through them.
In a smaller garden, consider using the ferns as your focal points with more delicate and lower-growing ground covers.
Natural moss is the perfect companion for a variety of ferns preferring the same slightly acid soil that many ferns enjoy.
Perennial moss-like ground covers such as Irish and Scotch moss are excellent substitutes as well as the many thyme varieties. (For a closer look at some of my favourite moss-like ground covers go here.)
Other plants to consider growing alongside ferns include hostas that, although a non-native, work extremely well with ferns.
The hostas’ bold foliage is set off nicely by the delicate foliage of most ferns. Just pay attention to the ultimate size of both the hostas and the ferns. The larger ferns can quickly bury the smaller hostas. Choose a hosta large enough to compete happily with the chosen ferns.
In her inspirational book, Foliage and Garden Design, Canadian gardening author Marjorie Harris describes her love for combining ferns and hostas in the garden.
“Hostas and ferns are two families of plants that are so versatile you can work them in with shrubs and under trees, providing you add lots of humus and water regularly if it’s dry shade. These two perennials are among my favourites and I’ve tried to incorporate plenty of them.”
Other plants that work well with ferns include: ornamental grasses, spring ephemerals like trilliums, dog-tooth violet and columbine.
Spring bulbs can also be grown to add a little colour early in the season before the ferns have fully emerged.
Black-eyed Susans are also a showstopper growing in drifts through the ferns.
In our front garden, I have a lovely group of columbine surrounded by maidenhair ferns growing next to a large mossy limestone boulder. The combination is a nice late spring vignette that catches my attention every time I pass by.
Some final thoughts on ferns
I’m not sure what it is about ferns that always catch my attention, whether they are growing wild in the woodlands, in the spring garden as they unfurl their delicate fronds, or in the garden centre where I am confronted by a host of must-have specimens.
At first glance they appear to have very little to offer. Maybe this is the reason ferns are sometimes overlooked by gardeners, especially beginner gardeners often focused on bright-coloured and showy flowers or similarly-coloured foliage.
Ferns will have none of that.
It’s all about shades of green, texture and a rugged hardiness when it comes to ferns. Sure, there are the silvery fronds of the Japanese painted fern, but they just can’t compete with those massive dinner-plate-sized dahlias, the bright reds of big-box geraniums or even the neon-like colours of today’s coleus.
Instead, ferns take a backstage and work hard to create a quiet, cool resting place for our eyes and our minds.
However, even in a fern garden, there is alsway room for a ‘pop’ of colour.
In fact, it is the ferns that will take the pop of colour to a whole other level.
Try adding a hanging basket or a raised container of brightly-coloured fuchsia to your fern garden to create a simple focal point and maybe create a natural area for your hummingbirds or butterflies to visit reguarly.
The hummers will enjoy the cool, quiet of the fern garden along with the added benefit of a free meal.
Be sure to include a perch either natural or store bought for the hummingbirds to rest above the ferns
Nearby, include a bench for you to sit and enjoy the solitude of the fern garden with the occasional visit from the hummingbirds.
Ferns enjoy a long history
If time is any indicator, there is little doubt that the fern garden will be a recipe for long-term success.
Ferns, in fact, can be traced back through fossil records to a time more than 100 million years before dinosaurs walked the earth. Ferns actually grew before any flowering plants even existed on earth. Today there are thousands of species of ferns, from the tiniest that grow just inches off the ground to massive tree ferns.
Thinking back, maybe there was something to that day I decided to crawl through our fern garden to get the feel for what animals experience on their daily jaunts through the ferns.
Maybe just a reminder that our gardens are not that far from those prehistoric times when dinosaurs roamed the earth.
And, a reminder that the ferns are among the few living things left of those times.
As an affiliate marketer with Amazon or other marketing companies, I earn money from qualifying purchases.